Smart device leak testing is critical for today’s consumer expectations of device reliability. The IP67/68 rating is becoming a common standard for all smart handheld and wearable devices. This rating comes from tests performed at either component or full assembly level. Sub component testing may include some of the following items.
- Microphones
- Speakers
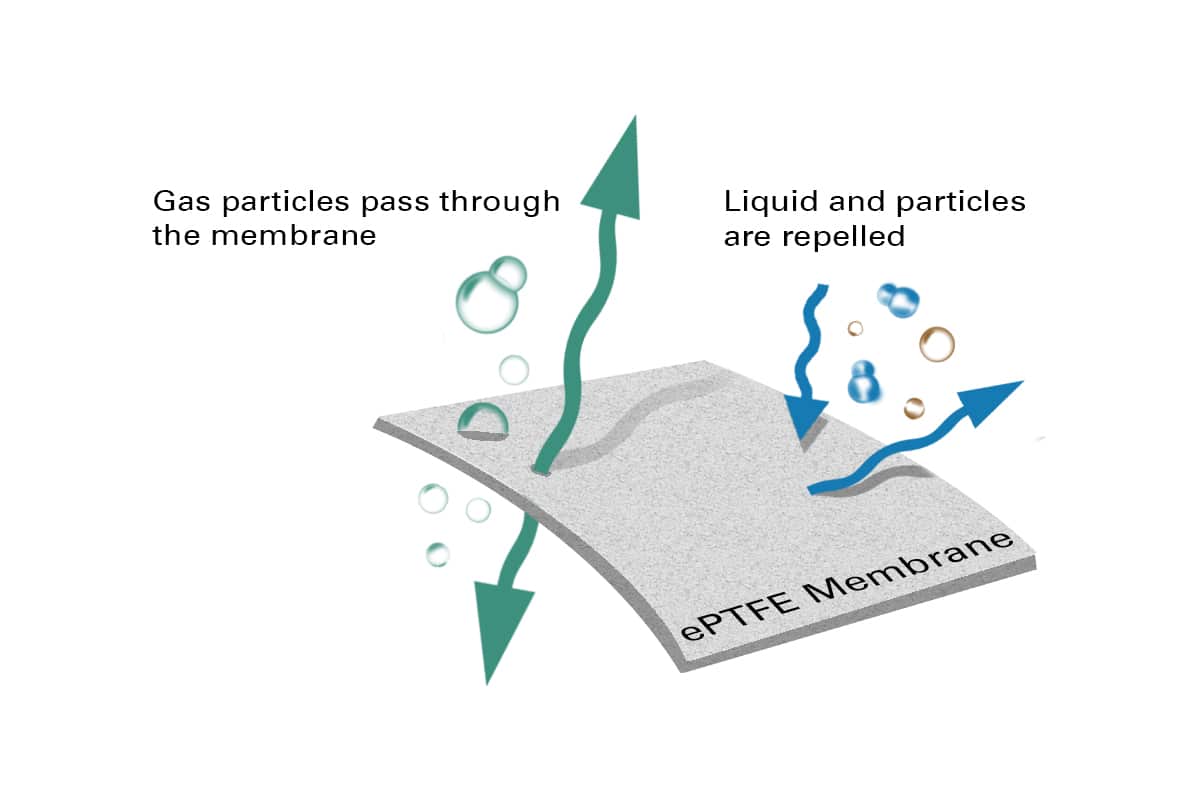
- ePTFE Membranes
- Barometric Vents
- Batteries



This testing occurs during the component manufacturing as well as before final assembly of the end product. The sub components are then also tested after assembly into their device housing. Furthermore, these device housings are sometimes tested for leaks. Some of these include.
- Power and Headphone Jacks
- Dials
- Exterior Buttons
- Antenna Cutout Locations
- Perimeter Seals
IP67/68 Testing
IP67/68 testing includes testing for water ingress, air seal and air flow. Water ingress testing measures water moisture passing through membranes or seals on the device. To achieve this we fill one side of the unit under test (UUT) with water. We then add additional air to simulate depth and measure for water moisture on the opposite side. Air seal testing consists of checking device seals for air leaks at different test pressures. Using a similar method used in our water ingress testing. Finally, air flow testing helps us verify component integrity. We combine water ingress and air flow testing techniques here. Using ePTFE membranes as barometric vents allows us to verify at certain flow rates that no water is passing through the membrane and only air. One machine can run each of these tests if sample size is small enough. If cycle time is a factor another option is to have one machine run many test positions and multiple sensors.
Smart Device Battery Testing
Smart device batteries are leak tested with very tight specifications. Due to the nature of a battery any leaking could have dangerous consequences.
Depending on the design of the battery and defect specification two testing options are available. Helium and Mass Extraction leak testing. Here, testing can take place at partial assembly to reduce final assembly failures.
Other test methods exist such as volatile organic compound (VOC). However, these methods have limitations in their reliable detectable defect size. Anything below 5µm have proven difficult to detect using VOC. Another problem with VOC is the inability to test some materials.
Helium is an option for Li batteries made up of a metal housing and limited external plastic. Detectable defect sizes can be as low as 0.2µm or 0.5µm and as high as 5µm.
Mass extraction testing can detect defects of 1µm and above for plastic pouch type batteries and metal housing batteries. Contact us to discuss the advantages to each type of testing in greater detail.
Pfeiffer Vacuum, Inc. can provide expertise and experience in all types of smart device testing. Our lab and engineering teams will work with you to develop leak specifications. We also conduct part testing of your parts at our facility to ensure a satisfactory testing environment. We provide you a complete solution proven to beat the competition in cycle time and repeatability.